The carbon cycle is a process that explains the movement and transformation of carbon in nature. Additionally, it is essential for the survival of living beings. Therefore, it involves the exchange of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, and terrestrial ecosystems. In this way, the carbon cycle plays a critical role in maintaining natural balance. Furthermore, plants convert carbon dioxide into oxygen through photosynthesis. Animals and humans, on the other hand, release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere through respiration. In this case, the use of fossil fuels can negatively affect the carbon cycle. Moreover, the carbon cycle is vital for understanding and controlling climate change. Additionally, oceans absorb carbon from the atmosphere, helping to maintain balance. For this reason, reducing carbon emissions is crucial for preserving the natural cycle.
Table of Contents
- What is the Carbon Cycle Briefly
- What is the Water Cycle
- What is the Nitrogen Cycle
- What Would Happen Without the Nitrogen Cycle
- What is the Global Carbon Cycle
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Carbon Cycle Briefly

The carbon cycle is a process that refers to the movement and transformation of carbon in nature. It also encompasses the exchange of carbon between plants, animals, humans and the atmosphere. Therefore, it plays a critical role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. In this way, it is a necessary system for the survival of living things. In addition, plants convert carbon dioxide into oxygen through photosynthesis. Furthermore, animals and humans release carbon into the atmosphere through respiration. In this case, the use of fossil fuels can damage the carbon cycle. However, the carbon cycle is crucial for understanding climate change. Furthermore, the oceans play an important role in storing and stabilizing carbon. Therefore, reducing carbon emissions is essential for environmental sustainability. In addition, recycling and energy conservation help to reduce carbon emissions.
What is the Water Cycle

The water cycle is a process that describes the continuous movement and transformation of water on Earth. It also involves the movement of water between the atmosphere, land and oceans. Therefore, it is critical for the continuity of life. In this way, it plays a fundamental role in maintaining natural balance. In addition, the water cycle starts with evaporation and continues with condensation. In addition, water returns to the earth’s surface through precipitation such as rain and snow. This creates groundwater and surface runoff. However, the water cycle also influences climate and weather events. In addition, plants return water to the atmosphere through transpiration.
What is the Nitrogen Cycle
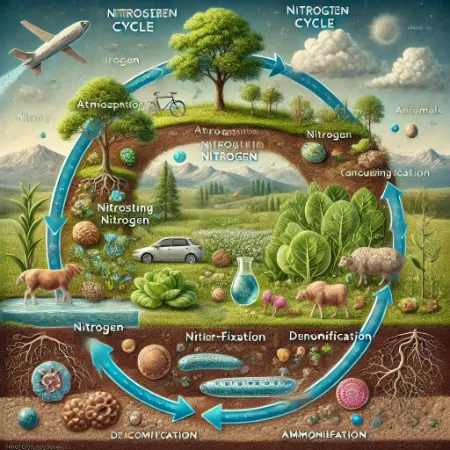
The nitrogen cycle is a process by which nitrogen is transformed between different forms in nature. It also involves the exchange of nitrogen between plants, animals and microorganisms. Therefore, it is vital for the survival of living things. In this way, essential molecules such as proteins and DNA are formed. In addition, nitrogen is free in the atmosphere and cannot be used directly by living things. Microorganisms bind nitrogen to the soil and make it available to plants. In this case, plants take up nitrogen for growth and development. However, animals meet their nitrogen needs through plants. Furthermore, with the death of the organisms, nitrogen returns back to the soil. Therefore, the nitrogen cycle plays a critical role for the productivity of ecosystems.
What Would Happen Without the Nitrogen Cycle
The nitrogen cycle is one of the fundamental elements of life, ensuring the balance of ecosystems. Furthermore, without the nitrogen cycle, the production of protein and DNA would not be possible. Therefore, plants would not grow and the food chain would be completely disrupted. In this case, basic food sources for animals and humans would run out. In addition, agricultural production would grind to a halt. Furthermore, infertile soils could lead to a food crisis. In this way, the world’s population could face serious hunger problems. However, free nitrogen in the atmosphere would remain unusable. Also, the cycle would be interrupted, as microorganisms would not have the function of binding nitrogen to the soil. Therefore, nature’s capacity for self-renewal would be completely lost. In addition, nitrogen deficiency would affect all species in ecosystems.
What is the Global Carbon Cycle
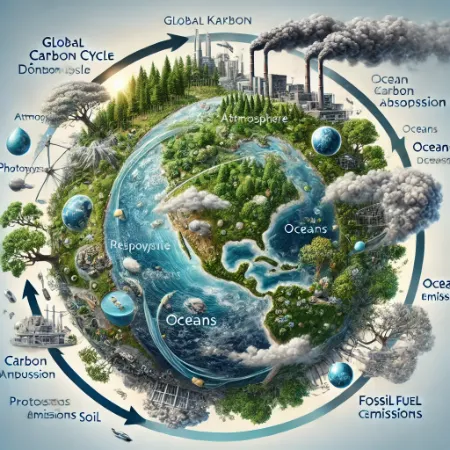
The global carbon cycle describes the movement of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, land and living things. It is also a vital process for keeping the world’s ecosystem in balance. Therefore, the carbon cycle plays a critical role in the sustainability of life. In this way, the amount of carbon in the atmosphere is kept in natural balance. In addition, plants absorb carbon from the atmosphere through photosynthesis. Humans and animals also release carbon through respiration. In this case, burning fossil fuels can damage the carbon cycle. However, the oceans maintain the balance by storing a significant amount of carbon. In addition, forests act as natural stores of carbon. Therefore, deforestation can negatively affect the carbon cycle. In addition, climate change can lead to serious imbalances in the carbon cycle.
Conclusion
The global carbon cycle is a critical process for maintaining the balance of the Earth’s ecosystem. It also regulates the movement of carbon between the atmosphere, land, oceans and living things. Therefore, imbalances in the carbon cycle can lead to serious problems such as climate change. In this case, it is crucial to reduce carbon emissions and protect natural storage sites. However, understanding and protecting the carbon cycle is a vital requirement for a sustainable future. In this way, a healthy environment for both ecosystems and human life can be ensured.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the global carbon cycle? The global carbon cycle is a process that describes the continuous movement of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, land and living things.
Why is the global carbon cycle important? The carbon cycle keeps the Earth’s ecosystem in balance and is critical for the sustainability of life.
What is the role of plants in the carbon cycle? Plants absorb carbon from the atmosphere through photosynthesis and produce oxygen, contributing to the natural cycling of carbon.
What role do oceans play in the carbon cycle? Oceans absorb and store carbon, helping to balance the amount of carbon in the atmosphere.
How do fossil fuels affect the carbon cycle? Burning fossil fuels increases the amount of carbon in the atmosphere and creates an imbalance in the carbon cycle.
How is the carbon cycle related to climate change? Imbalances in the carbon cycle can lead to climate change by increasing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
How does deforestation affect the carbon cycle? Forests are natural stores of carbon. Deforestation negatively affects the cycle by increasing the amount of carbon in the atmosphere.
What can be done to protect the carbon cycle? Reducing carbon emissions, protecting forests, using renewable energy sources support the carbon cycle.
How do human activities affect the carbon cycle? Human activities such as industry, agriculture and fossil fuel use disrupt the carbon cycle and have negative impacts on the environment.
Why is it important to understand the carbon cycle? Understanding the carbon cycle enables us to take the necessary steps for environmental sustainability and helps maintain the natural balance.